Biochem/physiol Actions Spiramycin is a 16membered ring macrolide antibiotic from Streptomyces ambofaciens It inhibits bacterial protein synthesis at the level of peptidytRNA dissociation from ribosomes It is mainly used against Grampositive bacteriaSpiramycin führt zu einer verminderten Oozystenausscheidung und zu einer Verbesserung der klinischen Symptome Es kann jedoch keine Heilung erreicht werden (Graczyk 1996a) Huhn, Trute, Fasan & Wachtel Spiramycin intramuskulär Sinusitis25 100 mg/kg während 2 7 e (Kroker 1999b) oral Mykoplasma gallisepticum100 0 mg pro Tier einmalig (Arzey 1992a) subkutanBuy high quality Spiramycin Adipate from toronto research chemicals Inc

Acetyl Spiramycin Biochemical Mybiosource
Spiramycin structure and chemical name
Spiramycin structure and chemical name-Spiramycin I contains total 136 bond(s);Spiramycin also induces a decrease in tritiated uridine (3HUdR) uptake, which suggests that Spiramycin interferes with an early event in the cell cycle 4 Spiramycin and, to a lesser extent, erythromycin increases total IL6 production without affecting IL1 alpha, IL1 beta, or tumor necrosis factor alpha production in human monocytes stimulated with lipopolysaccharide




Figure 2 From Genome Mining Of Streptomyces Ambofaciens Semantic Scholar
As a member of the wwPDB, the RCSB PDB curates and annotates PDB data according to agreed upon standards The RCSB PDB also provides a variety of tools and resources Users can perform simple and advanced searches based on annotations relating to sequence, structure and function These molecules are visualized, downloaded, and analyzed by users who range fromSpiramycin wird von Streptomyces ambofaciens synthetisiert und ist ein Makrolid mit einem 16gliedrigen Lactonring ( Kroker 1999b;Spiramycin Specification The Spiramycin, with the CAS registry number , is also known as Foromacidin It belongs to the product categories of Miscellaneous Natural Products;
Spiramycin I Molecular Formula C 43 H 74 N 2 O 14;Contact sites between protein and rRNA in 30S and 50S ribosomal subunits of Escherichia coli and Bacillus stearothermophilus were investigated at the molecular level using UV and 2iminothiolane as crosslinkers Thirteen ribosomal proteins (S3, S4, S7, S14, S17, L2, L4, L6, L14, L27, L28, L29, and L36) from these organisms were crosslinked in direct contact with the RNAs, and thePLQDGTZICFBBSODPUAUXBSSAN Spiramycin adipate Similar structures search, synonyms, formulas, resource links, and other chemical information
TIANFU CHEM Spiramycin Suppliers,provide TIANFU CHEM Spiramycin product and the products related with China (Mainland) TIANFU CHEM Spiramycin Henan Tianfu Chemical Co, Ltd China (Mainland) Welcome to LookChemcom Sign InJoin Free Home;Search Substances SPIRAMYCIN I 033ECH6IFG Possibly Marketed Outside US Source CanadaSPIRAMYCIN Source URLSpiramycin U contains total 133 bond(s);




Figure 3 Application Of Different Analytical Techniques And Microbiological Assays For The Analysis Of Macrolide Antibiotics From Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms And Biological Matrices
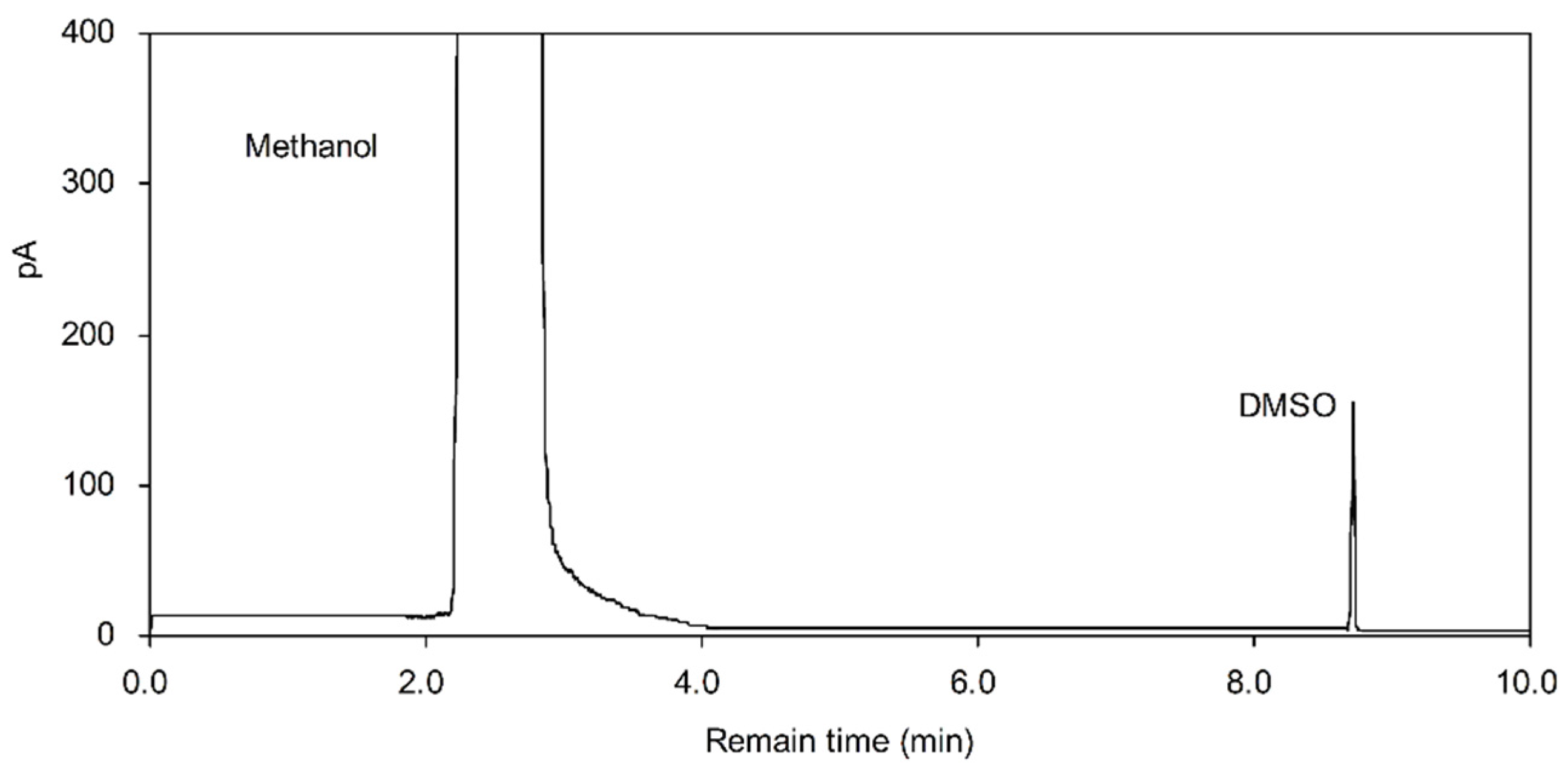



Applied Sciences Free Full Text Physicochemical Properties And In Vitro Dissolution Of Spiramycin Microparticles Using The Homogenate Antisolvent Precipitation Process Html
Monoisotopic mass Da;Spiramycin is a macrolide originally discovered as product of Streptomyces ambofaciens, with antibacterial and antiparasitic activities Although the specific mechanism of action has not been characterized, spiramycin likely inhibits protein synthesis by binding to the 50S subunit of the bacterial ribosomeChemical structure macrolide Application Spiramycin is a macrolide antibiotic that is commonly used to treat infections of soft tissues It has been used to treat bronchopulmonary infections in adults and has been used to study septicemia in mice Biochem/physiol Actions Spiramycin is a 16membered ring macrolide antibiotic from Streptomyces ambofaciens It inhibits bacterial



2



Spiramycin Toku E
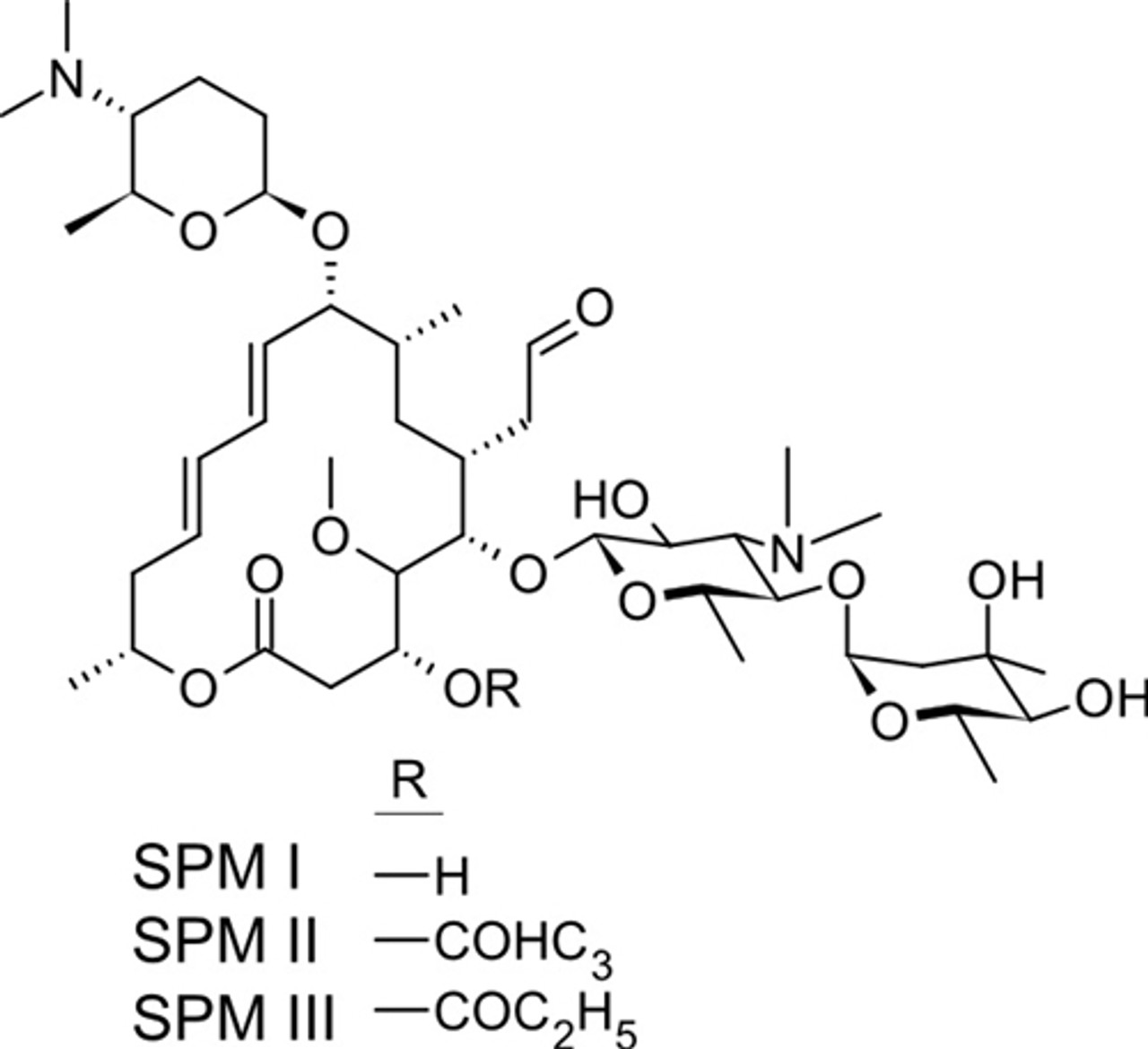
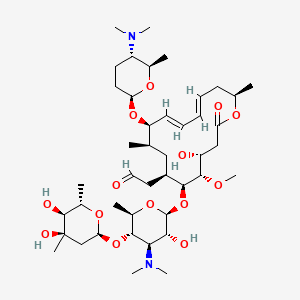
Spiramycin (C 43 H 74 N 2 O 14, M r = 8431 g/mol) wird aus bestimmten Stämmen von Streptomyces ambofaciens gewonnen oder nach anderen Verfahren hergestellt Die Hauptkomponente ist Spiramycin I Spiramycin II und II sind ebenfalls enthalten Spiramycin ist ein weisses bis schwach gelbliches Pulver, das in Wasser schwer löslich ist Wirkungen SpiramycinSpiramycin adipate C49H84N2O18 CID structure, chemical names, physical and chemical properties, classification, patents, literature, biological activities, safety/hazards/toxicity information, supplier lists, and moreCrystal structures of the Haloarcula marismortui large ribosomal subunit complexed with the 16membered macrolide antibiotics carbomycin A, spiramycin, and tylosin and a 15membered macrolide, azithromycin, show that they bind in the polypeptide exit tunnel adjacent to the peptidyl transferase center Their location suggests that they inhibit protein synthesis by blocking the



Spiramycin C43h74n2o14 Pubchem



Innate Adaptive And Cell Autonomous Immunity Against Toxoplasma Gondii Infection Experimental Molecular Medicine
Das Antibiotikum Spiromycin besitzt die chemische Summenformel C 43 H 74 N 2 O 14 Bei Zimmertemperatur liegt die Substanz als festes, kristallines Pulver vor In dieser Form besitzt einen leicht hygroskopischen Charakter, d h es zieht Wasser aus der Luft an In Wasser ist der Wirkstoff nur schwach löslichMolecular structure The molecular structure is based on structures generated from information available in ECHA's databases If generated, an InChI string will also be generated and made available for searching This information is only displayed if the substance is welldefined, its identity is not claimed confidential and there is sufficient information available in ECHA's databases for ECHA's algorithms to generate a molecular structureMacrolides (Antibiotics for Research and Experimental Use);



Spiramycin I C43h74n2o14 Chemspider




Spiramycin 8025 81 8
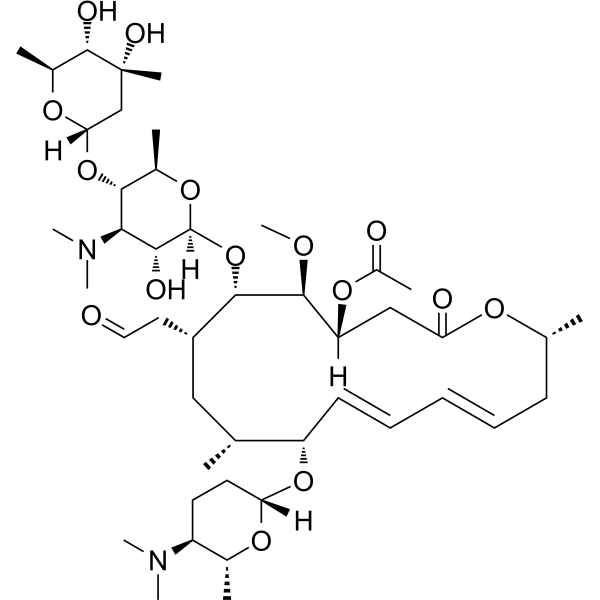
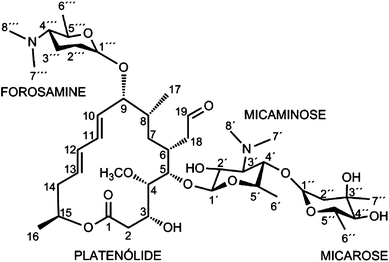
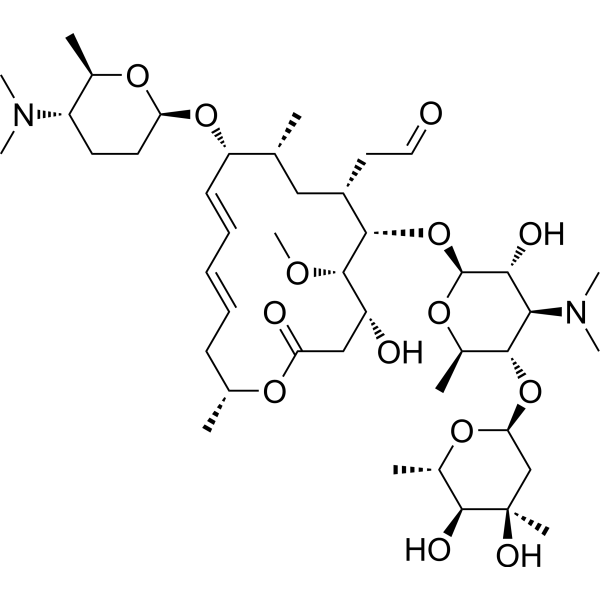
Spiramycin had been scientifically assessed again in November 1994 by the members of JECFA Spiramycin is a macrolide antibiotic used for the treatment and control of a number of bacterial and mycoplasmal infections in animals Spiramycin adipate and embonate were of low acute toxicity in the laboratory animals after oral orCocrystal Structure of Spiramycin bound to the 50S Ribosomal Subunit of Haloarcula marismortui Help Select a different viewer Citation Images created using Mol* should cite the PDB ID, the corresponding structure publication, Mol* (D Sehnal, S Bittrich, M Deshpande, R Svobodová, K Berka, V Bazgier, S Velankar, SK Burley, J Koča, AS Rose (21) Mol*Spiramycin (Rovamycin) is a macrolide antibiotic produced by Streptomyces ambofaciens with against bacteria and Toxoplasma gondii activities, and also has antiparasitic effect Spiramycin is composed of a 16member lactone ring, on which three sugars (mycaminose, forosamine, and mycarose) are attached Mechanism of Action & Protocol
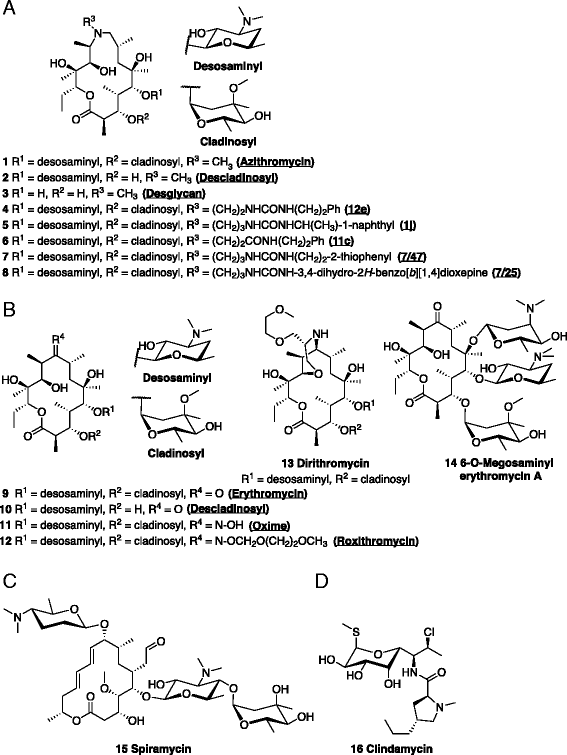



Macrolides Rapidly Inhibit Red Blood Cell Invasion By The Human Malaria Parasite Plasmodium Falciparum Bmc Biology Full Text




Spiramycin Iii Cas 52 7
An antibiotic used for the treatment and control of a number of bacterial and mycoplasmal infections in animals and also used as a growth promotor Availability status Introduction & key dates 00, Europe Examples of species treated Poultry, Sheep, Cattle, Pigs, Cats, Dogs Chemical structure IsomerismStructure activity relationships of spiramycins are discussed Introduction Spiramycin (PinnertSindico et al, 1955) is a complex of 16membered macrolide antibiotics active against Grampositive bacteria, mycoplasmas and toxoplasmas Its acetyl derivative in addition to spiramycin is used clinically Spiramycin contains threeView All Manufacturers & Suppliers of Spiramycin API with Drug Master Files (DMF), CEP/COS, Japanese DMFs, Written Confirmation (WC) details listed on PharmaCompasscom
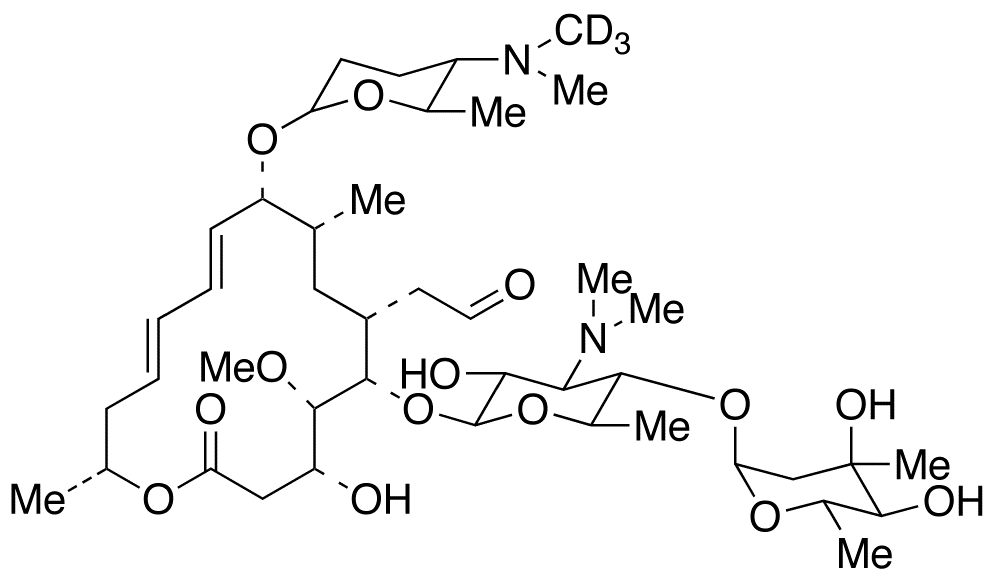



Spiramycin I D3 9 O 2r 5s 6r 5 Dimethylamino Tetrahydro 6 Methyl 2h Pyran 2 Yl Leucomycin V D3 Foromacidin A D3 Spiramycin A D3 C H D N O Trc



Spiramycin Rovamycin Tablets Iu 10 Pcs Cheap European And Russian Pharmacy Online Usa Uk Eu Asia Shipping
Spiramycin, a widely used veterinary macrolide antibiotic, was found at traceable levels (nanograms per litre range) in Po River water (NItaly) The aqueous environmental fate of this antibiotic compound was studied through drug decomposition, the identification of the main and secondary transformation products (TPs), assessment of mineralisation and the investigation Crystal structures of the Haloarcula marismortui large ribosomal subunit complexed with the 16membered macrolide antibiotics carbomycin A, spiramycin, and tylosin and a 15membered macrolide, azithromycin, show that they bind in the polypeptide exit tunnel adjacent to the peptidyl transferase center Their location suggests that they inhibit protein synthesis by62 nonH bond(s), 4 multiple bond(s), 11 rotatable bond(s), 4 double bond(s), 3 sixmembered ring(s), 1 ester(s) (aliphatic), 1 aldehyde(s) (aliphatic), 2 tertiary amine(s) (aliphatic), 4 hydroxyl group(s), 3 secondary alcohol(s), 1 tertiary alcohol(s) and 7 ether(s) (aliphatic) Learn more about Spiramycin I chemical structure at MolInstincts



2
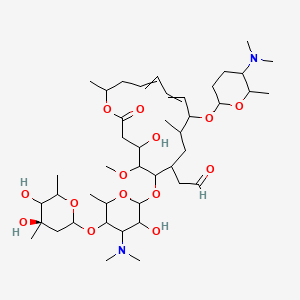



Rovamycin C43h74n2o14 Pubchem
The lack of aromaticity in the molecular structure of spiramycin did not encourage the formation of a complex with SnO 2 Pal In addition, cassiterite crystals deposited onto the palygorskite surface may have reduced the access to adsorption sites 3242 Metronidazole Metronidazole was largely retained by SnO 2 Pal (Fig 7B) The experimental data were properly Spiramycin ist ein natürliches Makrolid und besitzt einen 16gliedrigen Laktonring Der Wirkstoff ist ein Gemisch aus den drei Wirkstoffen Spiramycin A, B und C Der Wirkung kommt durch die Hemmung der Proteinbiosynthese durch Bindung an die 50sUntereinheit des bakteriellen Ribosoms zustande Demnach wirkt Spiramycin bakteriostatischSpiramycin I ChEBI ID CHEBI Definition A macrolide antibiotic produced by various Streptomyces species that is used to treat toxoplasmosis and various other infections of soft tissues Stars This entity has been manually annotated by the ChEBI Team Secondary ChEBI IDs




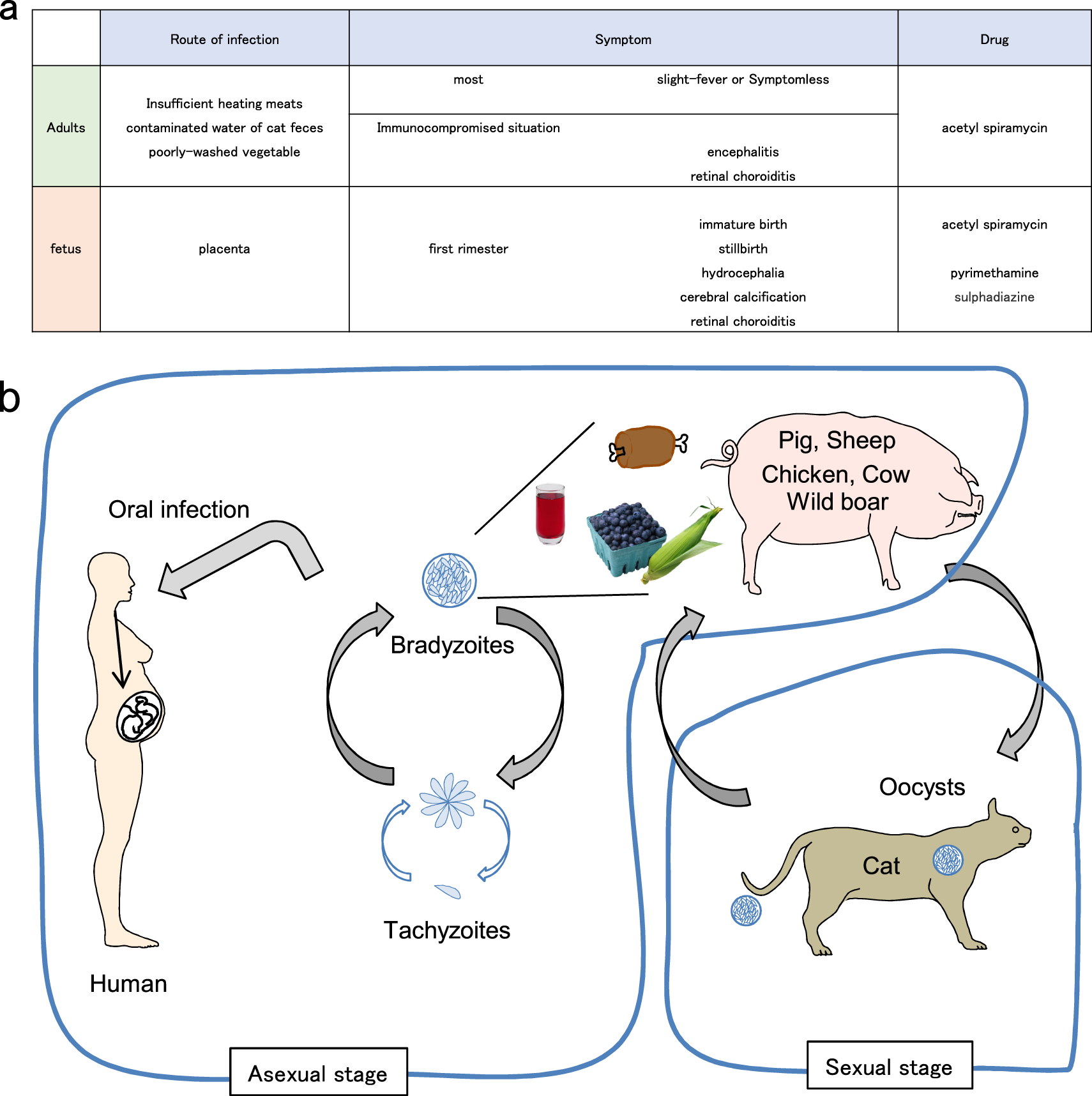
Significant Reduction Of Brain Cysts Caused By Toxoplasma Gondii After Treatment With Spiramycin Coadministered With Metronidazole In A Mouse Model Of Chronic Toxoplasmosis Abstract Europe Pmc



Spiramycin Drug Monograph Druginfosys Com
Antibiotics for Research and Experimental Use;Spiramycin was effective against a number of such strains in vivo, but erythromycin had little effect against these infections Investigation into the distribution of the antibiotics in the serum and tissues of mice showed that spiramycin was maintained in tissues (lung, liver, kidney, spleen and heart) at higher concentrations and for a longer period than erythromycin, although erythromycin1KD1 Cocrystal Structure Of Spiramycin Bound To The 50s Ribosomal Subunit Of Haloarcula Marismortui PDB ID 1KD1 Download MMDB ID PDB Deposition Date Updated in MMDB 07/10 Experimental Method xray diffraction Resolution 3 Å Source Organism Haloarcula marismortui Similar Structures VAST Download sequence data Biological Unit for




Efficient And Simple Hplc Method For Spiramycin Determination In Urine Samples And In Pharmaceutical Tablets Mahmoudi 18 Separation Science Plus Wiley Online Library




Figure 3 Application Of Different Analytical Techniques And Microbiological Assays For The Analysis Of Macrolide Antibiotics From Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms And Biological Matrices
Average mass Da;My LookChem Message Products;SummarySince the introduction of spiramycin, thousands of patients have been treated with the drug and few have developed severe adverse reactions Gastrointestinal disorders were usually mild and transient, and allergic reactions were quite uncommon Liver injury was described only once and drug interactions have not been reported The safety profile of this 16membered lactone




Spiramycin Search Results Mybiosource



Spiramycin スピラマイシン Drug Approvals International
Since the introduction of spiramycin, thousands of patients have been treated with the drug and few have developed severe adverse reactions Gastrointestinal disorders were usually mild and transient, and allergic reactions were quite uncommon Liver injury was described only once and drug interactions have not been reported The safety profile of this 16membered lactone ring macrolide derivative may reflect its chemical structureSanders 1994a ) Neospiramycin ist ein Demycarosilderivat von Spiramycin ( Sanders 1994a ) Es kann keinerlei Haftung für Ansprüche übernommen werden, die aus dieser Webseite erwachsen könnten4019 mass spectra in 6 spectral trees are available online for the compound Spiramycin Last modification occurred on PM mzCloud ‒ Free



Acetylspiramycin Spiramycin B Macrolide Antibiotic Medchemexpress



Scheme 1 Adenine Nucleotide Recognition By Spiramycin And Some Of Its Aromatic Derivatives Springerlink
We are Spiramycin CAS suppliers and specialize ,,, etcCHEBI spiramycin II A macrolide antibiotic produced by various Streptomyces species This entity has been manually annotated by the ChEBI Team No supplier information found for this compound A molecular entity capable of accepting a hydron from a donor (Br o nsted acid) A drug used to treat or prevent bacterial infectionsA macrolide antibiotic produced by Streptomyces ambofaciens The drug is effective against grampositive aerobic pathogens, N gonorrhoeae, and staphylococci It is used to treat infections



Spiramycin Rovamycin Antibiotic Medchemexpress
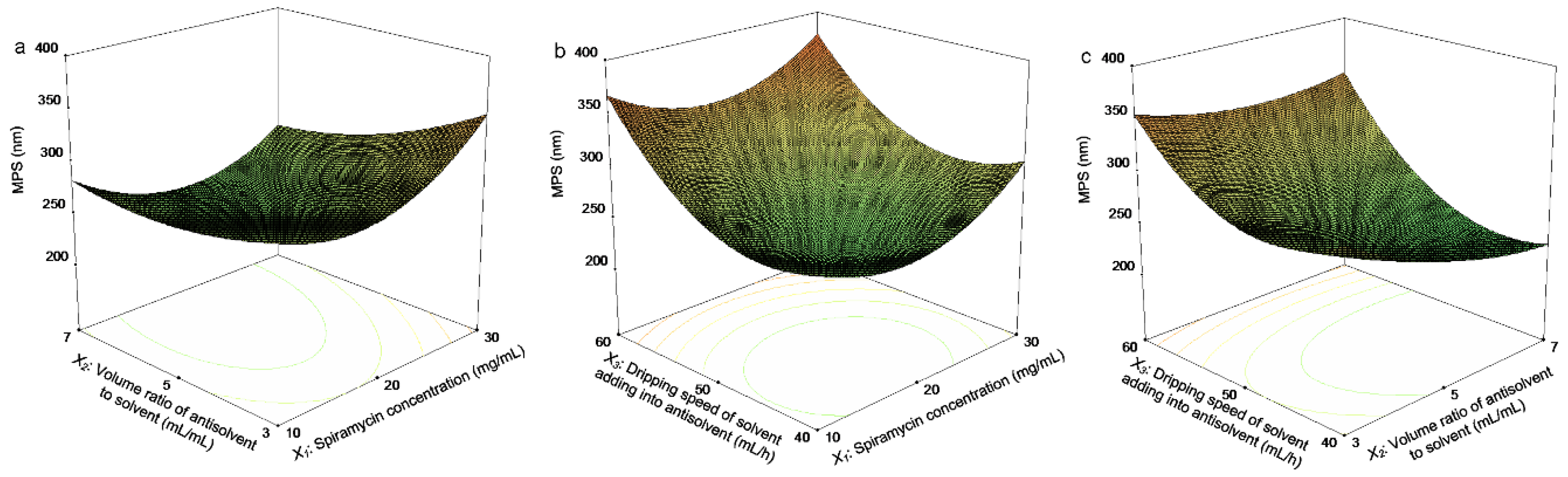



Applied Sciences Free Full Text Physicochemical Properties And In Vitro Dissolution Of Spiramycin Microparticles Using The Homogenate Antisolvent Precipitation Process Html
Spiramycin ist ein Makrolidantibiotikum Es wirkt gegen verschiedene Bakterienarten und kann auch bei Toxoplasmose eingesetzt werden Wirkung Spiramycin bindet an die 50SUntereinheit von Prokaryotischen RibosomenDer Mechanismus beobachteter Resistenzen ist noch nicht vollständig aufgeklärt und kann je nach Organismus unterschiedlich sein Definition62 nonH bond(s), 4 multiple bond(s), 10 rotatable bond(s), 4 double bond(s), 3 sixmembered ring(s), 1 ester(s) (aliphatic), 1 aldehyde(s) (aliphatic), 1 tertiary amine(s) (aliphatic), 6 hydroxyl group(s), 4 secondary alcohol(s), 2 tertiary alcohol(s) and 7 ether(s) (aliphatic) Learn more about Spiramycin U chemical structure at MolInstincts




Neo Spiramycin I Cas 62 2 Glentham Life Sciences




Spiramycin Formacidine Nsc Rovamycine Cas Number 8025 81 8 Cayman Chemical



Spiramycin Embonate C66h90n2o Pubchem



50 5 Spiramycin A Spiramycin I Foromacidin A 9 O 2r 5s 6r 5 Dimethylam



2




Chemical Structures Of Main Components Of Spiramycin And Its Related Download Scientific Diagram



Spiramycin A Reappraisal Of Its Antibacterial Activity Pdf Free Download
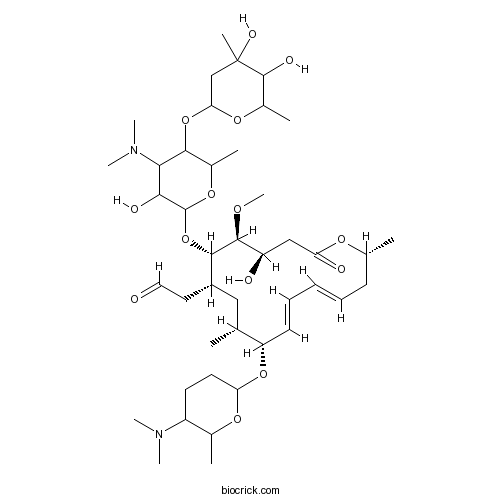



Spiramycin Cas 8025 81 8 High Purity Manufacturer Biocrick



Tables And Figures




Figure 2 From Genome Mining Of Streptomyces Ambofaciens Semantic Scholar




Polyamines Affect Diversely The Antibiotic Potency Journal Of Biological Chemistry




Structure Activity Relationships Of Ketolides Vs Macrolides Douthwaite 01 Clinical Microbiology And Infection Wiley Online Library
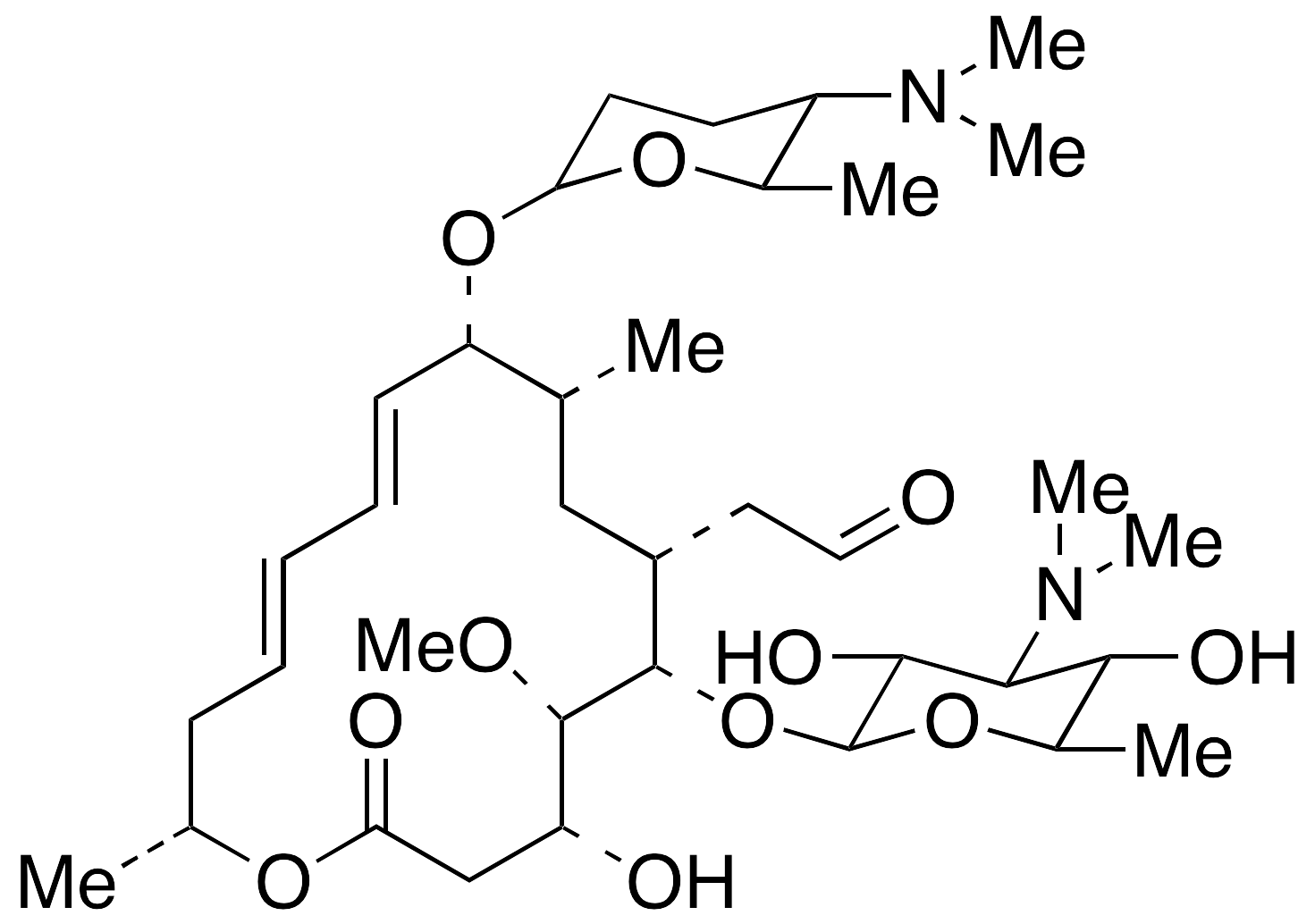



N 5mg Neo Spiramycin I 62 2 Generon




Spiramycin Iii Cas 52 7 Iii Antibiotic Medkoo
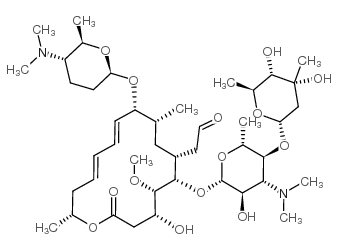



Spiramycin I Cas 50 5 Chemsrc
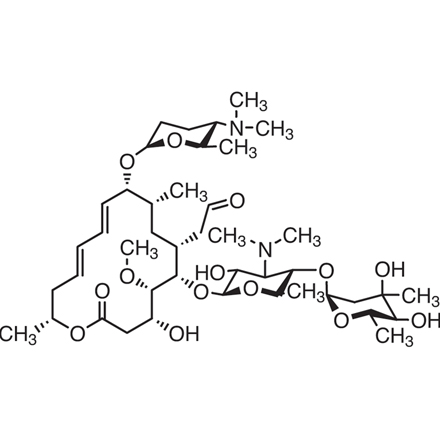



Spiramycin 8025 81 8 Tci Europe N V




Polyamines Affect Diversely The Antibiotic Potency Journal Of Biological Chemistry
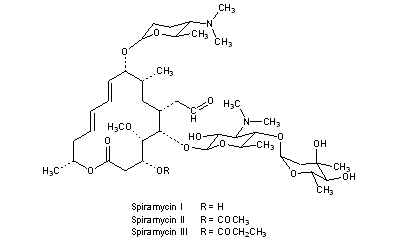



Spiramycin
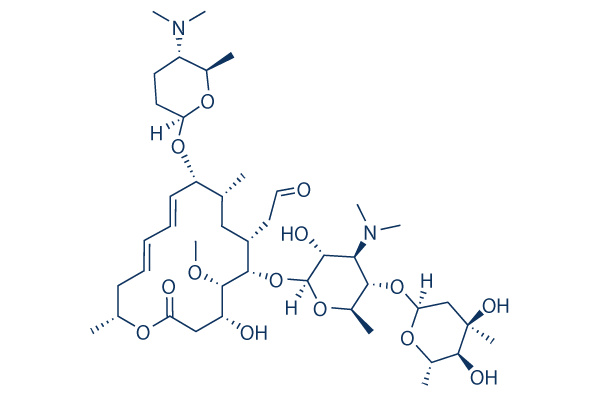



Spiramycin I 99 Hplc Selleck Antibiotics Chemical Qcfile



2




Spiramycin Biorbyt




Chemical Structure Of Obtained Spiramycin Derivatives Download Scientific Diagram




Figure 1 From Tissue Distribution Of Bitespiramycin And Spiramycin In Rats Semantic Scholar




Regulation Of The Biosynthesis Of The Macrolide Antibiotic Spiramycin In Streptomyces Ambofaciens Journal Of Bacteriology




Regulation Of The Biosynthesis Of The Macrolide Antibiotic Spiramycin In Streptomyces Ambofaciens Journal Of Bacteriology




Rcsb Pdb 1kd1 Co Crystal Structure Of Spiramycin Bound To The 50s Ribosomal Subunit Of Haloarcula Marismortui
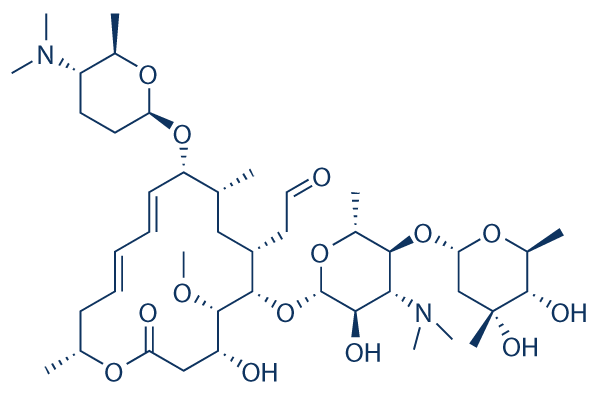



Spiramycin 99 Hplc Selleck Antibiotics Chemical




Pdf Effect Of Spiramycin And Tulathromycin On Abomasal Emptying Rate In Milk Fed Calves Peter Constable And Mohammad Hajikolaei Academia Edu
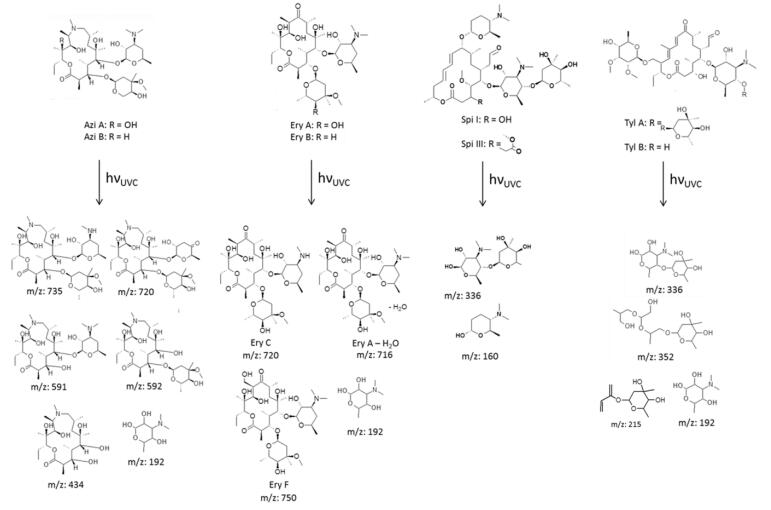



Elimination Of Macrolides In Water Bodies Using Photochemical Oxidation




Spiramycin Structure C43h74n2o14 Over 100 Million Chemical Compounds Mol Instincts




The Structures Of Four Macrolide Antibiotics Bound To The Large Ribosomal Subunit Sciencedirect




50 5 Spiramycin I Contains 6 Spiramycin Iii 9 O 2r 5s 6r 5 Dimethylamino Tetrahydro 6 Methyl 2h Pyran 2 Yl Leucomycin V Foromacidin A Spiramycin A C H N O Trc




Chemical Structures Of Main Components Of Spiramycin And Its Related Download Scientific Diagram




Spiramycin Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard Milliporesigma Supelco 500 Fisher Scientific
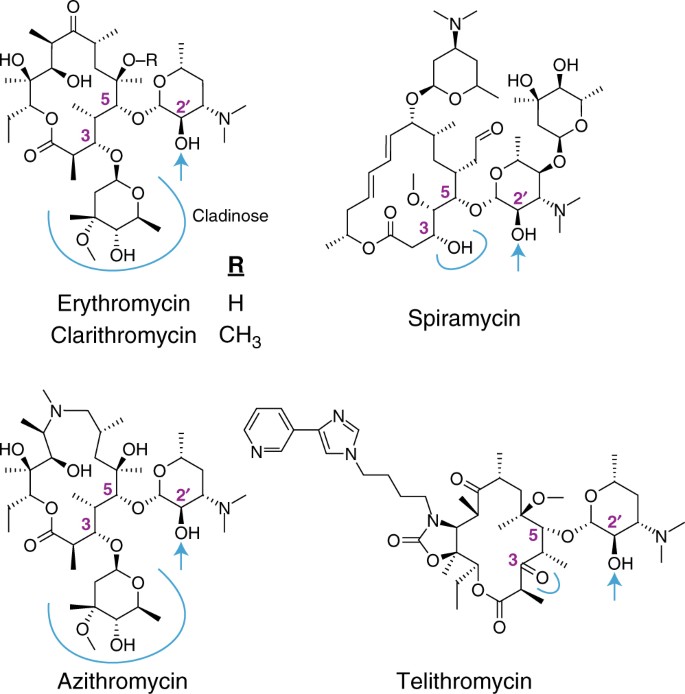



The Evolution Of Substrate Discrimination In Macrolide Antibiotic Resistance Enzymes Nature Communications




Spiramycin Hydrochloride C43h75cln2o14 Pubchem




Acetyl Spiramycin Biochemical Mybiosource



2
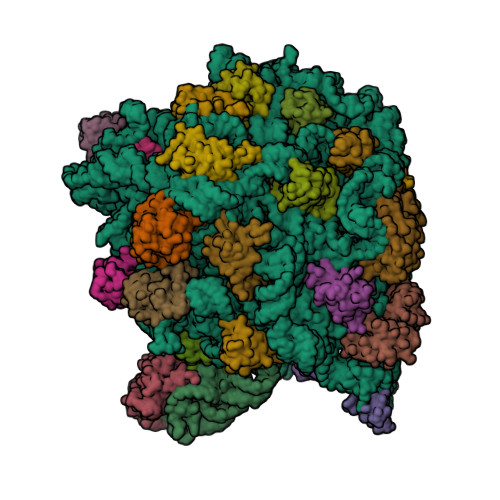



Rcsb Pdb 1kd1 Co Crystal Structure Of Spiramycin Bound To The 50s Ribosomal Subunit Of Haloarcula Marismortui




Spiramycin Ii



Q Tbn And9gcth3d8x1nireuodgfhyz04qsitlwdy5u24hqn3wfh7gfdgiknay Usqp Cau




Spiramycin Structure C43h74n2o14 Over 100 Million Chemical Compounds Mol Instincts
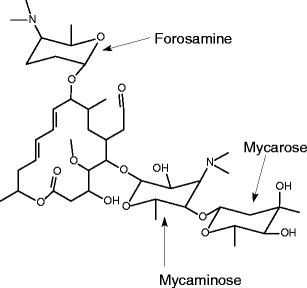



Fate Of Antibacterial Spiramycin In River Waters Springerlink




Rovamycine Spiramycin Buy Online




Antibacterial Inactivation Of Spiramycin After Titanium Dioxide Photocatalytic Treatment Sciencedirect




Spiramycin Adipate Cas 680 55 7 Chemsrc
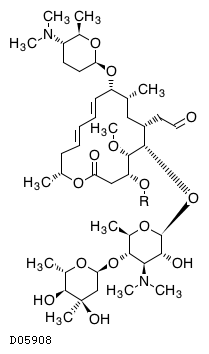



Kegg Drug Spiramycin




Pdf Determination Of Spiramycin And Neospiramycin Antibiotic Residues In Raw Milk Using Lc Esi Ms Ms And Solid Phase Extraction Pascal Sanders Academia Edu



Spiramycin 8025 81 8



1



Q Tbn And9gcr9ohc8k8xdklq3 Vpmbg8 G8izttazf3lfsyvoxor 7xtdmk Usqp Cau




Spiramycin Rovamycine Macrolide Antibiotic Cas 8025 81 8 Ab Abcam



Spiramycin スピラマイシン Drug Approvals International
/4ECE7900D4445432802585F90081B95E/$file/FS44433_structure.png)



Spiramycin Adipate 680 55 7 Biosynth Carbosynth Product




Spiramycin Biorbyt
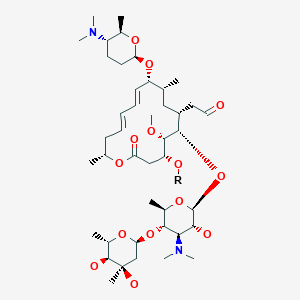



Spiramycin New Drug Approvals




Formacidine Absource Diagnostics
/D218B7AA3AA73D1B802585F8006742F1/$file/AS16859_structure.png)



Spiramycin I 50 5 Carbosynth Product



2




Spiramycin Adipate Properties Molecular Formula Applications Worldofchemicals



Anti Obesity Effects Of Spiramycin In Vitro And In Vivo




Structures Of Spiramycins Neospiramycins Spiramycins U And S And Download Scientific Diagram




Spiramycin Wikipedia




Acetyl Spiramycin Spiramycin Adipate Spiramycin Base Manufacturers And Suppliers Price Fengchen
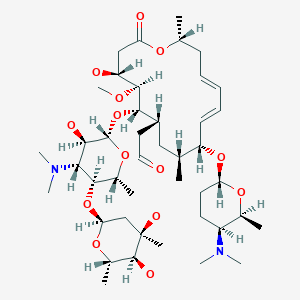



Spiramycin New Drug Approvals



2




Epa1 Levoisovalerylspiramycin Iii And Preparations Preparation Methods And Uses Thereof Google Patents



1
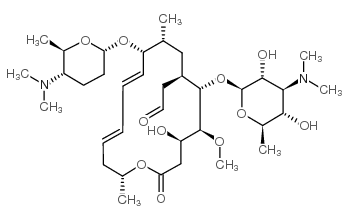



Neo Spiramycin I Cas 62 2 Chemsrc
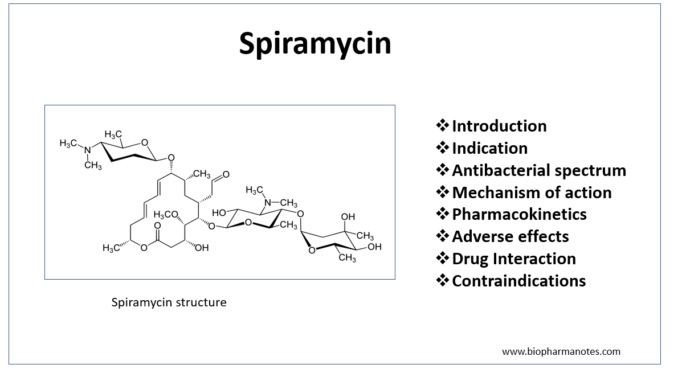



Pharmacology Of Spiromycin Biopharma Notes




Clarithromycin Wikipedia




Acetyl Spiramycin Biochemical Mybiosource




Spiramycin Adipate 680 55 7 Wiki




Structure Activity Relationships Of Ketolides Vs Macrolides Clinical Microbiology And Infection




Spiramycin I 50 5




Rapid Thermal Acid Hydrolysis Of Spiramycin By Silicotungstic Acid Under Microwave Irradiation Sciencedirect




Kegg Drug Spiramycin Adipate
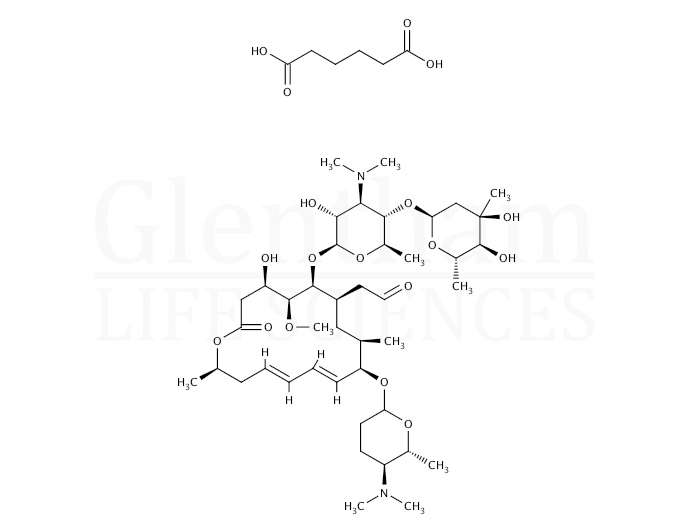



Spiramycin Adipate 680 55 7 7w Gp97 Cymit Quimica S L
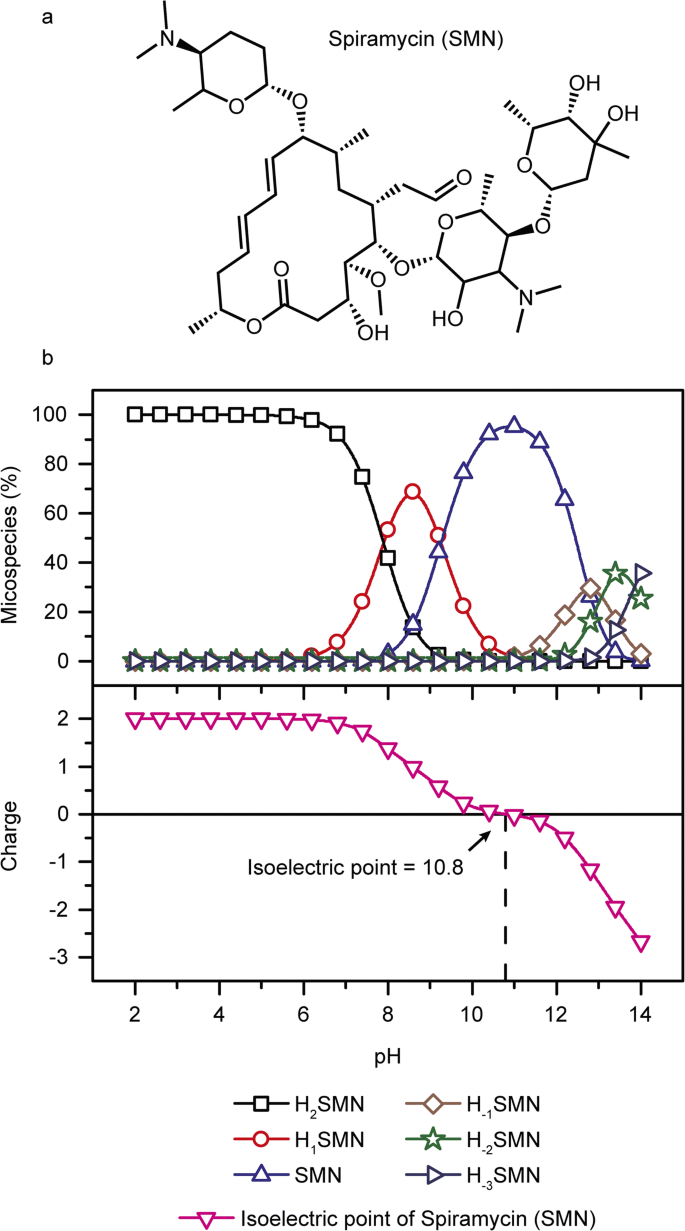



Spiramycin Adsorption Behavior On Activated Bentonite Activated Carbon And Natural Phosphate In Aqueous Solution Springerlink
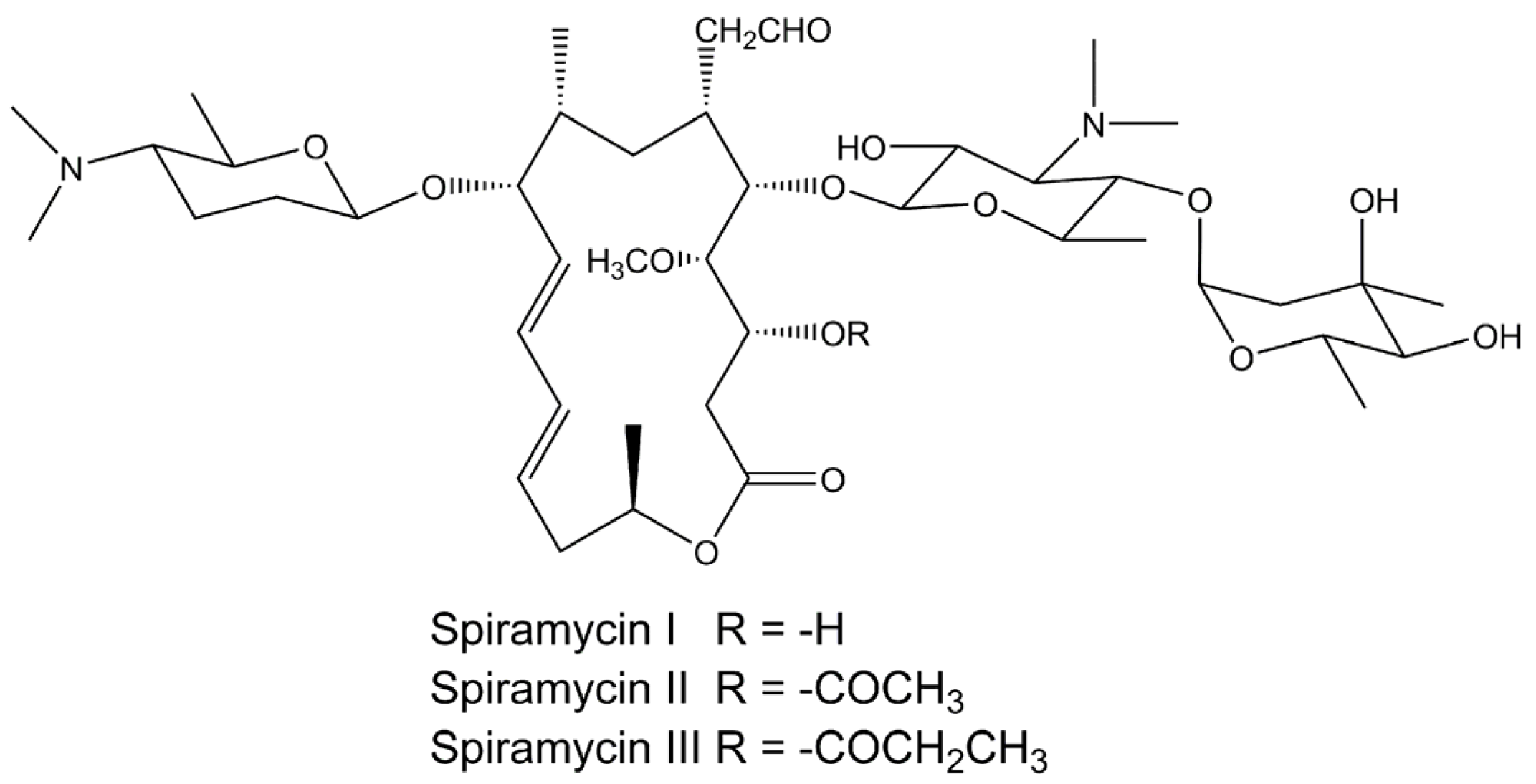



Applied Sciences Free Full Text Physicochemical Properties And In Vitro Dissolution Of Spiramycin Microparticles Using The Homogenate Antisolvent Precipitation Process Html



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿